A vitamin is an organic compound and a vital nutrient that an organism requires in limited amounts. An organic chemical compound (or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained through the diet; thus, the term vitamin is conditional upon the circumstances and the particular organism.
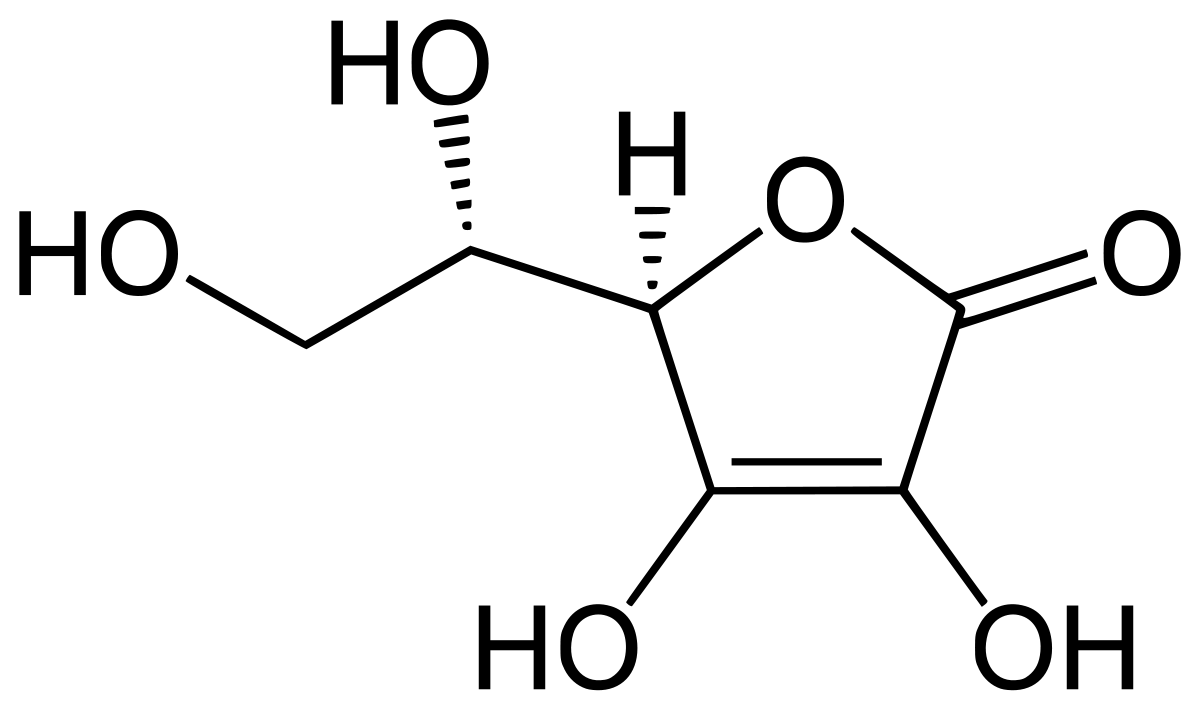
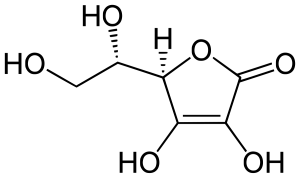
Ascorbic acid (one form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal organisms.
Several human vitamins have benefits for the skin (e.g. Vitamin E / Tocopherol, Pro-vitamine B5 / Panthenol, Vitamin C / Ascorbic Acid).
Vitamin C is reknown in cosmetology and dermatology for the many benefits it provides to the skin : it is an important antioxidant that protects the skin by scavenging and destroying free radicals and reactive oxygen-derived species. It could improve the morphogenesis of dermal epidermal junction, and is also known for its skin lightening properties. As an UV photoprotection agent, it also has a synergistic effect when used in conjunction with vitamin E, a lipophilic vitamin. Vitamin C is also used topically because of its ability to reduce wrinkles by promoting collagen synthesis and its skin-depigmenting activity.